Whole Genome Sequencing (WGS)
For Personalised Healthcare at MYOriGene
At MyOriGene, we are proud to offer a thoughtful and innovative approach to personal health insights through out Whole Genome Sequencing (WGS) technology. Our non-invasive DNA test kits are designed with your comfort and convenience in mind, allowing you to discover comprehensive information about your genetic makeup in a simple, stress-free manner.
Whole Genome Sequencing is more than just a DNA test, it’s an exploration into your unique genetic story. This advanced method meticulously examines your entire DNA, covering over 3 billion base pairs, to provide a detailed picture of your genetic health and traits. It is an opportunity to gain deeper insights into your personal health and well-being in a way that traditional DNA tests cannot match. Let us dive deeper on what WGS is in this article.

What is Whole Genome Sequencing?
Whole Genome Sequencing (WGS) is a sophisticated and extensive genetic analysis technique that deciphers the complete DNA sequence of an individual’s genome. This includes all the coding and non-coding regions of their DNA, providing an extensive genetic profile. The significance of WGS lies in its ability to uncover genetic variations and insights that were previously inaccessible.
Whole-genome sequencing can find different types of changes in your DNA.
One notable application of WGS in DNA test kits is for ultra-comprehensive health insights. By examining the entire genome, WGS can identify both common and rare genetic variants that may influence an individual’s health.
1. Single Nucleotide Variants
This means it can spot the tiniest changes in the building blocks of your DNA.
2. Insertions/Deletions
It can also notice which parts of your DNA are added or removed.
3. Large Structural Variants
It’s even able to detect big changes in the way your DNA is arranged.
4. Copy Number Changes
It can tell if you have too many or too few copies of certain parts of your DNA.
Understanding the Differences
A common point of confusion in genomics is the difference between the three DNA sequencing techniques. All 3 techniques involve sequencing an individual’s DNA, but they target different portions of the genome. There are 3 types of DNA sequencing technologies available on the market:
Compare with :
Percentage of Genome Covered
Data Obtained
Lifetime Results
(does not require retesting)
Year Discovered

SNP Genotyping
Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms
0.03%
Genomic variations only
No
(Require Retesting)
Late 1990s to Early 2000s
WES
Whole Exome Squencing
1-2%
Surface-level exome only
No
(Require Retesting)
Early 2000s


WGS
Whole Genome Sequencing

100%
Entire genome
Yes
Fully sequenced in 2022





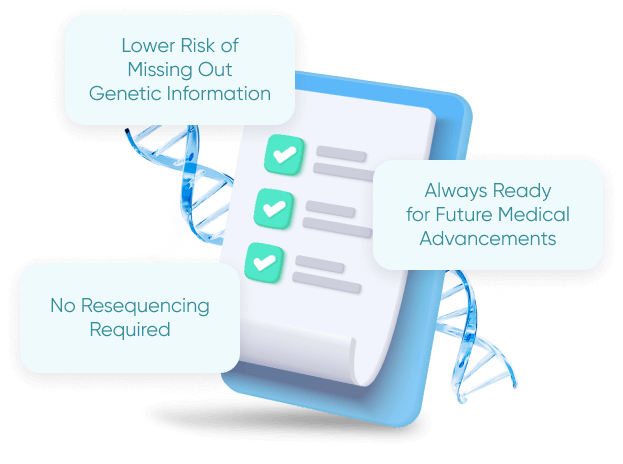
Why Scan 100% of the Genome?

Lower Risk of Missing Out Genetic Information
Always Ready for Future Medical Advancements
No Resequencing Required
1 Time DNA Sequencing, Lifetime Comfort
For WGS, you only need to sequence your DNA once in your entire lifetime and scientists can revisit your data again any time in the future when new medical discoveries are made. This is not the case for SNP Genotyping and WES where you need to conduct resequencing (as in, taking a DNA test again) When new discoveries are made.
As of 2022, the whole human genome has been fully sequenced. This means that SNP Genotyping and WES that only map 0.03 – 2% of the human genome are technologies of the past.
Advantages of WGS
Over WES and SNP Genotyping

Detection Of Non-Coding Variants
WGS can identify variations in non-coding regions of the genome, which play crucial roles in regulating gene expression and can be associated with diseases.

Broader Range Of Genetic Conditions
WGS can reveal a wider spectrum of genetic conditions, including rare diseases with no known genetic markers.
Comprehensive Structural Variant Detection
WGS excels in detecting structural variations, such as large insertions, deletions, and rearrangements in the genome, which may contribute to genetic disorders.

Holistic Genetic Understanding
By examining the entire genome, WGS provides a more holistic understanding of an individual's genetic predispositions, offering insights into disease risks, pharmacogenomics, and ancestry.
The Uses of WGS Now and in the Future
For WGS, you only need to sequence your DNA once in your entire lifetime and scientists can revisit your data again any time in the future when new medical discoveries are made. This is not the case for SNP Genotyping and WES where you need to conduct resequencing (as in, taking a DNA test again) when new discoveries are made.

Precision Medicine
WGS is paving the way for personalised medicine, allowing for tailored treatment plans based on an individual's unique genetic profile

Early Disease Dectection
With advancements in bioinformatics, WGS can potentially detect diseases at earlier stages, enabling timely intervention.

Research Advancements
WGS is a cornestone of genomic research, helping scientists better understand the genetic basis of diseases and potentially uncovering novel therapeutic targets.

Genomic Medicine
As costs decrease and technology improves, WGS may become a routime part of healthcare, guiding preventive measures and treatment decision.
In Conclusion
Whole Genome Sequencing is a transformative technology with profound implications for personalised healthcare. Its ability to provide a comprehensive view of an individual’s genetic makeup, detect non-coding variants, and uncover a wide range of genetic conditions makes it a powerful tool in the realm of genetics and genomics. As the field of genomics continues to advance, WGS promises to play an increasingly crucial role in improving healthcare outcomes and advancing our understanding of the human genome.
For more information on WGS and its applications, you can refer to our genetic lab partners at Alps Globemedic

